Japan’s ispace aims to make moon travel accessible for all
SpaceX has long been a leader in the private space industry, but now, investors are looking to Japan for a new challenger. Ispace, a Japanese space startup, is gaining attention for its ambitious plans to launch missions to the moon.
Ispace was founded in 2010 by Takeshi Hakamada, a former employee of the Japanese space agency JAXA. The company’s goal is to establish a lunar colony by 2040, and it’s well on its way to achieving that. Ispace has already secured $95 million in funding from investors like Innovation Network Corporation of Japan, and it’s planning to launch its first lunar mission in 2022.
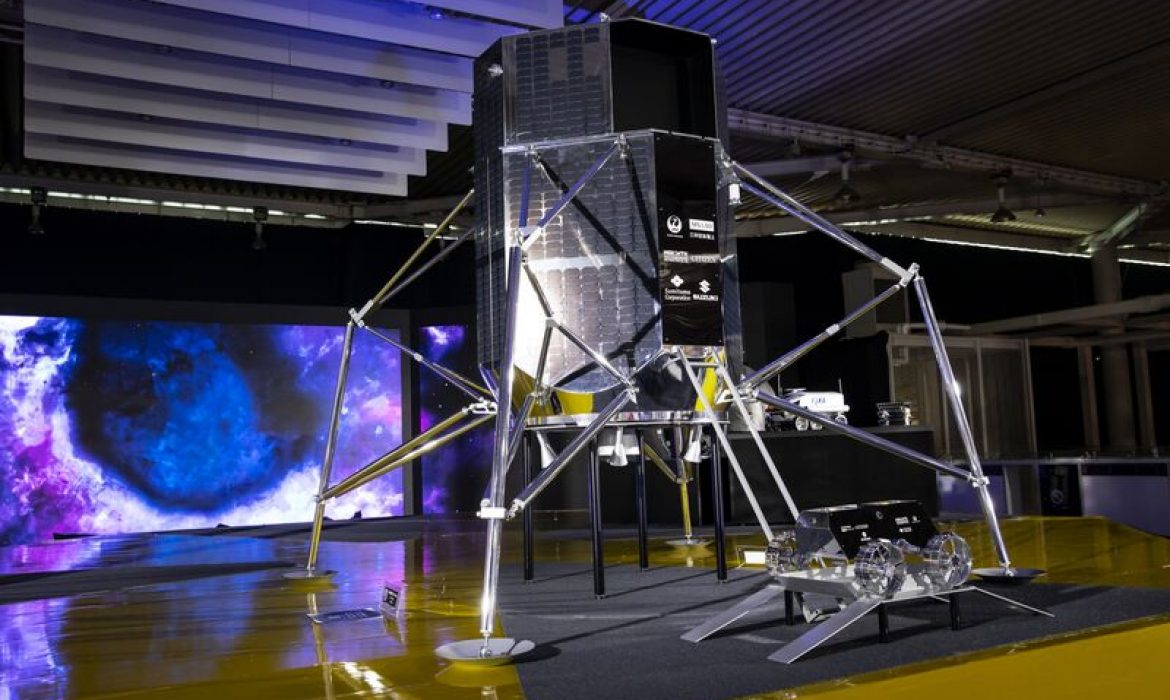
Ispace’s first mission, dubbed “Hakuto-R,” will involve sending a lunar lander to the moon’s surface to collect data and images. The company is also planning a second mission, “Hakuto-C,” in 2023, which will attempt to land a rover on the moon. If successful, it would make Ispace the first private company to land a rover on the moon.
Ispace’s success so far has attracted attention from investors around the world. The company recently announced that it had raised an additional $46 million in funding, bringing its total funding to over $140 million. The new funding will be used to develop a new spacecraft, the Hakuto-F, which will be capable of carrying a crew of up to four people to the moon.
Ispace is not the only company trying to break into the private space industry. There are many other startups, like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic, that are also trying to launch missions to space. But Ispace’s unique approach to lunar exploration has caught the attention of investors who are eager to get in on the ground floor of a potential industry leader.
Ispace has also secured partnerships with some big names in the aerospace industry. The company has a contract with Elon Musk’s SpaceX to launch its lunar lander on a Falcon 9 rocket. Ispace has also partnered with Draper, a company that specializes in space navigation and guidance systems, to develop the technology needed to land its rover on the moon.
Ispace’s ambitious plans have not gone unnoticed by the Japanese government. In fact, the company has received significant support from the government, which sees Ispace as a key player in the future of Japan’s space industry. In 2019, the government announced that it would be investing $180 million in Ispace over the next few years to help the company develop its lunar exploration technology.
Ispace’s success so far is a testament to the growing interest in private space exploration. As more companies enter the industry, the competition is heating up, and investors are keeping a close eye on the space startups that they believe have the potential to become the next big thing. For Ispace, the sky’s the limit, and it will be interesting to see where the company goes from here.
OpenAI under fire: FTC receives complaints about AI development practices.
OpenAI, the leading artificial intelligence research organization, has received a complaint from the Federal Trade Commission, or FTC.
The FTC, backed by entrepreneur Elon Musk, has been a strong advocate of slowing the development of artificial intelligence because of concerns about its potential risks to humanity. The complaint alleges that OpenAI acted in violation of antitrust laws by engaging in anti-competitive practices.
OpenAI, founded in 2015 by a group of tech luminaries including Elon Musk, is at the forefront of developing advanced AI technology. The organization’s mission is to create artificial intelligence that is safe and useful for humanity. However, the FTC’s complaint states that the company may be using methods that stifle competition and prevent others from developing in this field.
This news comes at a time when the debate about the risks and benefits of artificial intelligence is heating up. Some experts argue that the rapid development of AI could lead to disastrous consequences if the technology falls into the wrong hands. Others see AI as a powerful tool that can help solve some of the world’s most pressing problems.
It remains to be seen how this complaint will end and how it will affect the future of AI research. One thing is certain: the debate about the risks and benefits of AI is far from over, and it will remain a hot topic for years to come.